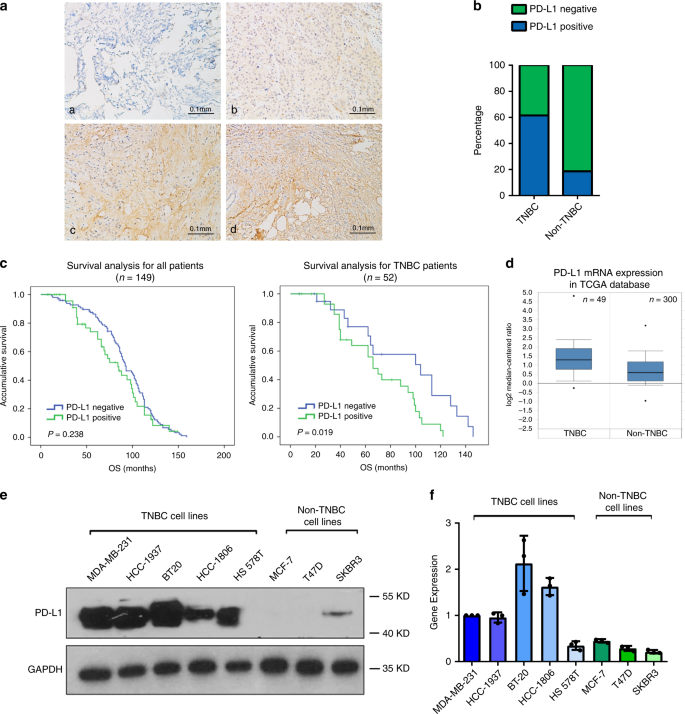
PD-L1 expression in multiple breast cancer cell lines was evaluated to identify intrinsic differences that affect their potential for immune evasion. This study was undertaken to determine whether PD-L1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer TNBC and to investigate the loss of PTEN as a mechanism of PD-L1 regulation.
 Npm1 Upregulates The Transcription Of Pd L1 And Suppresses T Cell Activity In Triple Negative Breast Cancer Nature Communications
Npm1 Upregulates The Transcription Of Pd L1 And Suppresses T Cell Activity In Triple Negative Breast Cancer Nature Communications
There is little consensus on the methods used to evaluate PD-L1 expression immunohistochemically and this may contribute to the diverging results found in this study.
Pdl1 breast cancer. Further investigation of PD-L1 expression in breast cancer and its effect on prognosis is required. Some authors advocate that PD-L1 expression may help in breast cancer prognosis. On March 8 2019 the Food and Drug Administration granted.
Triple-negative breast cancer is breast cancer that is. Owing to the aggressive nature and the emergence of resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs patients with TNBC have a worse prognosis than other subtypes of breast cancer. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the regulation of programmed death ligand 1 PDL1 lactate dehydrogenase A LDHA and miR-34a in triple negative breast cancer TNBC and to explore the function and mechanism of PDL1 and LDHA as competitive endogenous RNAs ceRNAs in TNBC via regulation of miR-34a.
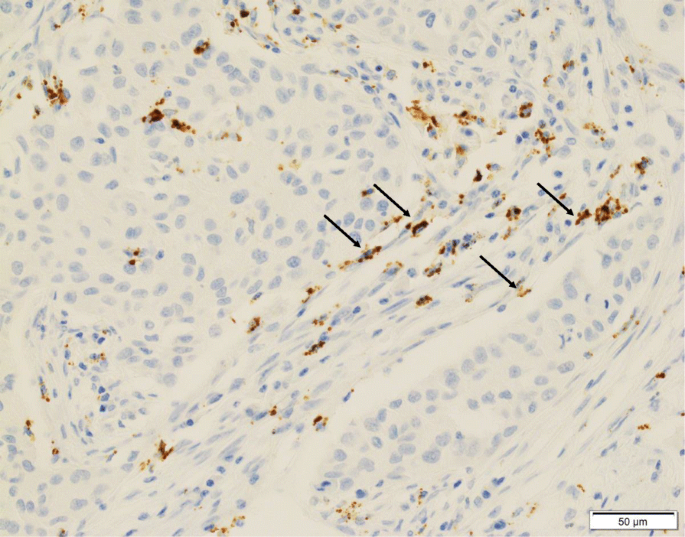
In triple-negative breast cancer PD-L1 is primarily expressed on tumor-infiltrating immune cells rather than on tumor cells themselves. To form a secondary recurrent andor metastatic tumor a breast cancer cell must evade the innate and adaptive immune systems. Regarding the role of platinum in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer CALGB 40603 is likely the trial most relevant to clinical decision-making at this time.
Launched in 2016 the VENTANA PD-L1 SP142 Assay is the primary diagnostic assay within the Tecentriq clinical development program and was used to enroll and stratify patients in Tecentriq clinical trials. To form a secondary recurrent andor metastatic tumor a breast cancer cell must evade the innate and adaptive immune systems. With the introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors in breast cancer there is an increased interest in PD-L1 as a predictive and prognostic marker.
Schmid noted that more than half of the patients in the experimental arm who were PD-L1 positive were alive at 2 year versus 37 of controls. Triple-negative breast cancers are usually more aggressive harder to treat and more likely to come back recur than cancers that are hormone-receptor-positive or. This study was undertaken to determine whether PD-L1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer TNBC and to investigate the loss of PTEN as a mechanism of PD-L1 regulation.
Programmed cell death 1 PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 are key physiologic suppressors of the cytotoxic immune reaction. PD-L1 expression was associated with response to NAC with trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Early-phase trials targeting the T-cell inhibitory molecule programmed cell death ligand 1 PD-L1 have shown clinical efficacy in cancer.
He added that atezolizumab plus nab- paclitaxel is approved by the FDA and is recommended for treatment of patients with PD-L1 IC metastatic triple negative breast cancer in the NCCN guidelines. CD47 enables cancer cells to evade killing by macrophages whereas CD73 and PDL1 mediate independent mechanisms of evasion of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA RNA sequencing data showed significantly greater expression of the PD-L1.
However conflicting data have been reported on the prognostic role of protein expression while few studies have investigated the prognostic value of PD-L1 gene expression. FDA approves atezolizumab for PD-L1 positive unresectable locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Tumor cells express programmed death ligand 1 PD-L1 and is a key immune evasion mechanism.
CD47 enables cancer cells to evade killing by macrophages whereas CD73 and PDL1 mediate independent mechanisms of evasion of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies in women worldwide and one of the leading causes of cancer-related death. With cancer vaccines the.
Clinical efficacy in cancer. Triple-negative breast cancer TNBC is characterized by the lack of clinically significant levels of estrogen receptor ER progesterone receptor PR and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 HER2. In conclusion 175 of HER2-positive type patients were PD-L1-positive.
